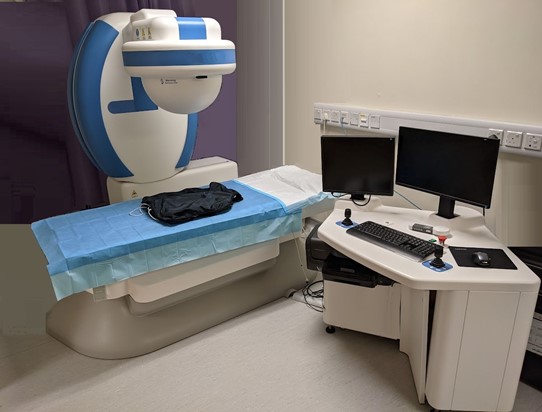
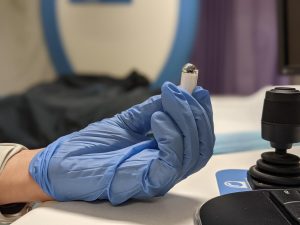

1. What is magnet-controlled capsule endoscopy?
This is a sedation-free and minimally invasive endoscopic modality for examining oesophagus, stomach and small bowel. Patients will swallow a magnetic capsule with a build-in camera for gastrointestinal examination. During the stomach examination, the capsule can be guided precisely through the external magnetic controller in five dimensions. It takes about 10 to 20 minutes for stomach examination. Then capsule will transit into duodenum, jejunum, ileum with gastrointestinal peristalsis and will be naturally passed out during bowel opening. Images are captured and recorded at 2 frames per second. The battery life is up to 12 hours.
2. Who can undergo magnet-controlled capsule endoscopy?
- Those who intend to have health check
- Those who are indicated for conventional endoscopy, but are unwilling to have or cannot tolerate this procedure. For example, upper abdominal pain, bloating, acid reflux, gastrointestinal bleeding (e.g. melena, hematemesis), allergy to sedatives or anaesthetics.
- Those who are suspected of small bowel disease without stenosis or obstruction, especially those with negative findings in oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD) and colonoscopy.
Magnet-controlled capsule endoscopy is mainly used for screening and diagnosis. If there is a need for biopsy or therapeutic intervention, doctors will arrange conventional endoscopy for further management. A previous study found magnet-controlled capsule endoscopy detected gastric focal lesions in the whole stomach with 90.4% sensitivity and 94.7% specificity. It did not miss any lesions of significance (including tumors or large ulcers). [1]
3. Who is not suitable for magnet-controlled capsule endoscopy?
- Patients who have a pacemaker, electronic cochlear implant or other metal implants that are contraindicated to MRI scans.
- Pregnant women
- Children
- Gastrointestinal obstruction, stenosis, perforation, or fistula
- Dysphagia
- Patients who have undergone gastric bypass or bariatric surgery and who are expected with high risk of capsule retention.
4. The risk of magnet-controlled capsule endoscopy
The major risk is capsule retention in the body (rare scenario).
5. Differences between magnet-controlled capsule endoscopy and OGD
| OGD
|
Magnet-controlled capsule endoscopy | |
| If there is a need to use anaesthetics or sedatives | Yes
|
No |
| Pain | Yes | No |
| If it can induce gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation | Yes | No |
| Cross infection | Yes | No (Disposable capsule) |
| The coverage of examination | Esophagus, stomach, duodenum | Esophagus, stomach, whole small bowel |
| Should discontinue anticoagulants before the procedure? | Yes | No |
| Can you work during the examination? | No | Yes (After completion of the stomach examination) |
| Purpose | Diagnosis, biopsy and therapeutic intervention | Screening and diagnosis |
6. The differences between magnet-controlled capsule endoscopy and conventional capsule endoscopy
Magnet-controlled capsule endoscopy allows active navigation by the operator during the stomach examination, while the conventional capsule endoscopy scans the stomach by passive transiting resulting in large blind areas.
7. The process of magnet-controlled capsule endoscopy examination
- The examinee should fast for 8 hours and follow instructions to drink defoamer and 800ml water 40 minutes before the examination.
- Wear a wireless data recorder, lay on the examination bed and swallow the capsule.
- The examinee will be instructed to change position to facilitate the stomach examination when an operator in the control console navigate the capsule in the body.
- After the stomach examination, the examinee can wear data recorder to leave the room. The capsule will passively transit to the rest of the gastrointestinal tract and transmit captured images to the data recorder on the way until the battery is used up (battery life >10 hours).
- Return the data recorder.
FAQ:
- Is the capsule difficult to swallow?
It is a pill-sized (about 27mm X 18mm) capsule with a smooth surface. Except those with dysphagia, most patients have no difficulties in swallowing the capsule.
- Can I choose the examination coverage? How long does the examination last?
The examinee can choose:
- Esophagus and stomach The examination is usually completed within 30 minutes.
- Esophagus, stomach and the whole small bowel examination. The examination requires bowel preparation. The whole examination usually needs 10-12 hours.
- Can I drink and eat during the examination?
Yes. Examinee can drink water or any colourless liquid during examination and resume a normal diet after the examination. Examinee who chooses whole small bowel examination can eat solid food (e.g. sandwich) 4-6 hours after stomach examination.
Reference:
1. Liao Z, Hou X, et al. Accuracy of Magnetically Controlled Capsule Endoscopy, Compared With Conventional Gastroscopy, in Detection of Gastric Diseases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Sep;14(9):1266-1273.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.05.013. Epub 2016 May 20. PMID: 27211503.



